Soft implantable microelectrodes for future medicine: prosthetics, neural signal recording and neuromodulation
Abstract
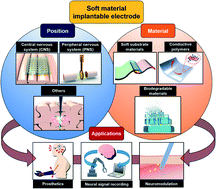
Implantable devices have provided various potential diagnostic options and therapeutic methods in diverse medical fields. A variety of hard-material-based implantable electrodes have been developed. However, several limitations for their chronic implantation remain, including mechanical mismatches at the interface between the electrode and the soft tissue, and biocompatibility. Soft-material-based implantable devices are suitable candidates for complementing the limitations of hard electrodes. Advances in microtechnology and materials science have largely solved many challenges, such as optimization of shape, minimization of infection, enhancement of biocompatibility and integration with components for diverse functions. Significant strides have also been made in mechanical matching of electrodes to soft tissue. In this review, we provide an overview of recent advances in soft-material-based implantable electrodes for medical applications, categorized according to their implantation site and material composition. We then review specific applications in three categories: neuroprosthetics, neural signal recording, and neuromodulation. Finally, we describe various strategies for the future development and application of implantable, soft-material-based devices.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Lab on a Chip Recent Review Articles and Implantable Devices

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...