Dietary supplement based on stilbenes: a focus on gut microbial metabolism by the in vitro simulator M-SHIME®
Abstract
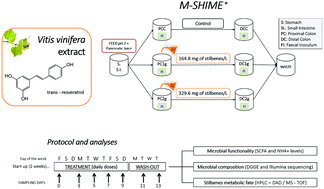
Polyphenols and intestinal microbiota can influence each other, modifying metabolism and gut wellness. Data on this mutual effect need to be improved. Several studies on the biological activities of resveratrol and derivatives have been carried out, but the effects of a continuous administration of stilbenes on gut microbiota have not yet been investigated. This study evaluated the effects of an extract from Vitis vinifera, containing a combination of t-resveratrol and ε-viniferin, on intestinal microbiota, using the advanced gastrointestinal simulator M-SHIME®. A triple M-SHIME® experiment was performed using two concentrations of the extract (i.e. 1 and 2 g L−1), simulating a continuous daily intake. The effects were evaluated in terms of microbial functionality (SCFA and NH4+) and composition (DGGE and Illumina sequencing), since the microbiological aspect has been less considered so far. The treatment induced changes in microbial functionality and composition. In fact, the levels of SCFA and NH4+ suffered a strong decrease (i.e. inhibition of the saccharolytic and proteolytic activity), while DGGE and Illumina showed important modifications of the microbiota composition, associated with an imbalance of the colonic microbiota (i.e. increase in the relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae). HPLC-DAD-TOF-MS analyses demonstrated that the metabolism of t-resveratrol and other stilbenes was inhibited by continuous administration. Our results suggest M-SHIME® as an explorative tool to define the dosage of food supplements, in particular to simulate effective continuous administration in humans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...