Xanthohumol-induced presynaptic reduction of glutamate release in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
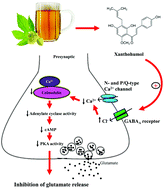
This study examined whether xanthohumol, a hop-derived prenylated flavonoid present in beer, affects glutamate release in the rat hippocampus. In the rat hippocampal nerve terminals (synaptosomes), xanthohumol inhibited the release of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP)-evoked glutamate and the elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, whereas it had no effect on 4-AP-mediated depolarization. The inhibitory effect of xanthohumol on the evoked glutamate release was prevented by removing extracellular Ca2+, using the Cav2.2 (N-type) and Cav2.1 (P/Q-type) channel blocker ω-CgTX MVIIC, the calmodulin antagonists W7 and calmidazolium, and the protein kinase A inhibitor H89; however, no such effect was observed when the G-protein inhibitor N-ethylmaleimide was used. In addition, immunocytochemical data demonstrated that GABAA receptors are present in the hippocampal synaptosomes and that the xanthohumol effect on evoked glutamate release was antagonized by the GABAA receptor antagonist SR95531. Furthermore, in slice preparations, xanthohumol reduced the frequency of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents without affecting their amplitude. We conclude that xanthohumol acts at GABAA receptors present in the hippocampal nerve terminals to decrease the Ca2+ influx through N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels, which subsequently suppresses the Ca2+-calmodulin/PKA cascade to decrease the evoked glutamate release.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...