Polyethylenimine promoted electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO in aqueous medium by graphene-supported amorphous molybdenum sulphide†
Abstract
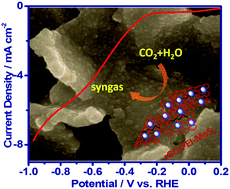
Efficiently and selectively converting CO2 to value-added carbon compounds remains a major challenge in sustainable energy research. In this paper, we report the synthesis of a cost-effective catalyst, i.e. amorphous molybdenum sulphide on a polyethylenimine modified reduced graphene oxide substrate, for electrocatalytically reducing CO2 into CO in CO2 saturated aqueous NaHCO3 medium with high efficiency and selectivity. The catalyst is capable of producing CO at overpotentials as low as 140 mV and reaches a maximum faradaic efficiency of 85.1% at an overpotential of 540 mV. At an overpotential of 290 mV with respect to the formation of CO, it catalyzes the formation of syngas with high stability. Detailed investigations reveal that PEI works as a co-catalyst by providing a synergetic effect with MoSx.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...