Probing the effects of the ester functional group, alkyl side chain length and anions on the bulk nanostructure of ionic liquids: a computational study†
Abstract
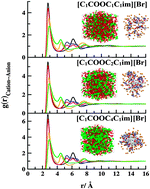
The effects of ester addition on nanostructural properties of biodegradable ILs composed of 1-alkoxycarbonyl-3-alkyl-imidazolium cations ([C1COOCnC1im]+, n = 1, 2, 4) combined with [Br]−, [NO3]−, [BF4]−, [PF6]−, [TfO]−, and [Tf2N]− were explored by using the molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) analysis at 400 K. Various thermodynamic properties of these ILs were extensively computed in our earlier work (Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, 54, 11678–11700). Nano-scale segregation analysis demonstrates the formation of a small spherical island-like hydrocarbon within the continuous ionic domain for ILs with short alkyl side chain ([C1COOC1C1im]), and a sponge-like nanostructure for the compound with long alkyl side chain ([C1COOC4C1im]). Ester-functionalized ILs with ethyl side chain ([C1COOC2C1im]) are the turning point between two different morphologies. Non-polar channels were observed for [C1COOC4C1im] ILs composed of smaller anions such as [Br] and [NO3], whereas clustering organization was found for the other anions. Formation of the spherical micelle-like nanostructure was seen for lengthened cations. Finally, the incorporation of an ester group into the alkyl side chain of the cation leads to stronger segregation between charged and uncharged networks, which consequently increased the possibility of self-assembly and micelle formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...