Relationship between vesicle size and steric hindrance influences vesicle rupture on solid supports†
Abstract
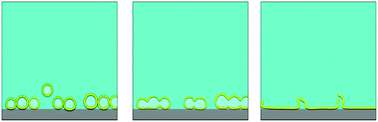
Phospholipid assemblies on solid supports mimic the cell membrane, and provide a platform to study membrane biology. Among the different types of model membranes, the planar bilayer is a two-dimensional lipid bilayer sheet that can be formed by the adsorption and spontaneous rupture of vesicles. The formation process is influenced by the interactions between vesicles and the solid support as well as between vesicles. On silicon oxide, which is a commonly used solid support, vesicles typically adsorb until reaching a critical coverage and then spontaneous rupture begins. Although it is generally understood that spontaneous rupture leads to planar bilayer formation, oversaturation of vesicles at the critical coverage can hinder the whole process due to a steric factor. To date, the role of this factor has been scrutinized only in relation to temperature, and the influence of additional parameters remains to be elucidated. In this work, we have investigated how vesicle size and corresponding steric constraints influence the kinetics of vesicle adsorption and rupture and, more specifically, how the state of adsorbed vesicles after fusion depends on the vesicle size. Using quartz crystal microbalance-dissipation (QCM-D) and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP), we characterized the adsorption kinetics of vesicles onto silicon oxide and the lateral mobility of solid-supported lipid assemblies. While the vesicle adsorption kinetics were diffusion-limited up to the onset of vesicle rupture, the extent of rupture depended on vesicle size and it was observed that larger vesicles are more prone to steric effects than smaller vesicles. We discuss this finding in terms of the structural transformation from adsorbed vesicles to a planar bilayer, including how the interplay of thermodynamic, kinetic and steric factors can affect vesicle rupture on solid supports.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...