The effect of complexing agents in chemical solution deposition of metal chalcogenide thin films
Abstract
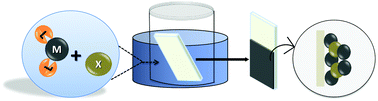
Among the chemical deposition methods to produce thin films, chemical deposition from aqueous solution (CD) is the oldest and most studied process in which the substrate is exposed to soluble precursors which react or decompose to produce the desired thin film material. An intricate balance of growth parameters is necessary to produce a good quality film. The presence of complexing agents ensures effective complexation of the metal cation in solution, leading to its slow release for preventing bulk precipitation. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the different complexing agents used to achieve control over the resultant morphology of CD metal chalcogenide thin films.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Materials Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...