Molecular modeling and spectroscopic study of quinone–protein adducts: insight into toxicity, selectivity, and reversibility†
Abstract
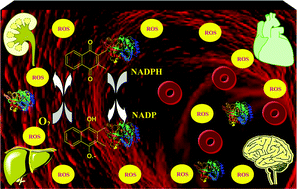
The important biological and toxicological roles of quinones could be attributed to their versatile electrophilic and oxidative properties. Quinones are able to undergo Michael addition with cellular thiols such as glutathione and proteins, and promote electron transfer in living systems via redox-cycling. Although the protein adduction of quinones is assumed to be a part of their metabolic fate, the adducts retain the redox-cycling capability of the parent quinones, and thus we can consider the adducts as a type of active metabolite. Herein, the toxicity, reversibility, and selectivity of protein adducts were studied using molecular spectroscopy and molecular modeling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...