Electrically driven assembly of CdTe quantum dots into photoconductive microwires†
Abstract
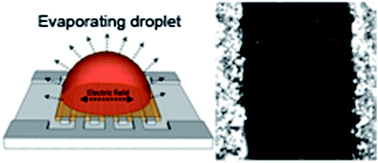
A low strength alternating current (AC) electric field applied across a drying aqueous CdTe nanoparticle suspension above 100 μm gap interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) allows rapid assembly of quantum dots into photoconductive microwires. The fabrication procedure is scalable for commercial photoelectronic applications as it does not require organic solvents, lengthy ligand-removal procedures, expensive microfabrication strategies or any sophisticated instrumentation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...