Introduction of VEGF or RGD sequences improves revascularization properties of Bombyx mori silk fibroin produced by transgenic silkworm
Abstract
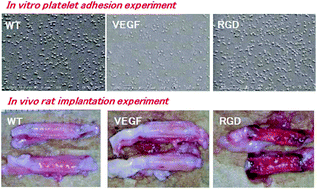
Bombyx mori silk fibroin (SF) was successfully used for vascular grafts implanted in rats or dogs. Current transgenic technology can be developed to produce SF with improved properties. In this study, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or the repeated fibronectin-derived sequence, TGRGDSPAS, and arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) were introduced into the SF heavy chain to improve its properties. A blood compatibility assay was performed to study lactose dehydrogenase (LDH) activity for both transgenic and wild type SF. Growth of human umbilical endothelial cells (HUVECs) showed greater enhancement of cellularization behaviour for the transgenic SF samples (VEGF and RGD) than for the wild type (WT) SF. VEGF SF also showed lower platelet adhesion than the RGD SF and WT SF. An in vivo implantation study supported these in vitro results. In particular, early endothelialisation was observed for VEGF transgenic SF, including the occurrence of native tissue organization at three months after implantation in rat abdominal aorta.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...