Hybrid fullerene conjugates as vectors for DNA cell-delivery†
Abstract
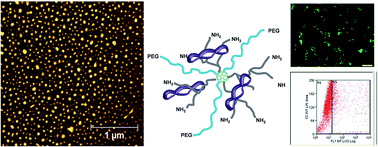
The present study reports fullerene conjugates that act as efficient binders of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) into cytofriendly polyplexes. The conjugates are designed to generate dendrimeric structures, having C60 as the core and bearing linear or branched PEI and polyethyleneglycol (PEG) arms (∼2 kDa). Simple and reproducible synthesis pathways provided C60-PEI and C60-PEG-PEI conjugates. They were able to bind linear and plasmidic dsDNA and they form particulate polyplexes of 50 to 200 nm in diameter. The resulted polyplexes toggle between the anionic and cationic state at nitrogen to phosphorous ratios (N/P) of about 5, as revealed by their zeta potential and became colloidally stable at N/P ratios above 10, as determined by atomic force microscopy (AFM). They are electrophoretically unbreakable starting with N/P ratios of 3 and of 5 when salmon sperm DNA and pEYFP-C1 plasmid, respectively are loaded. Both C60-PEI·pEYFP and C60-PEG-PEI·pEYFP polyplexes are non-cytotoxic against HEK 293T cells in culture and exhibit transfection efficiency better than 25% (N/P ratios above 20) and 6% (N/P ratios above 60) respectively, measured by flow cytometry. For comparison, the commercial SuperFect® from Qiagen (positive control) was able to provide an efficiency of 15–20%, under similar conditions. Moreover, the C60-PEG-PEI conjugate is as performant as the positive control in terms of expression of EYFP reporter gene in cultured cells and exhibited high cytocompatibility, determining cell proliferation up to 200%. Our study proved that C60-PEG-PEI is effective vector for DNA delivery being, in addition, easily synthesizable, practically non-cytotoxic and as efficient the commercially available transfection tools.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...