Quatsomes for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm
Abstract
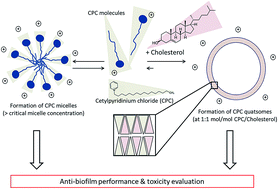
The anti-biofilm effect of drug delivery systems composed of the antiseptic quaternary ammonium compound cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) and cholesterol was evaluated in Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Self-assembly of CPC/cholesterol to approximately 100 nm CPC-quatsomes was successfully accomplished by a simple sonication/dispersion method over a broad concentration range from 0.5 to 10 mg ml−1 CPC. CPC-quatsomes showed a dose-dependent anti-biofilm effect, killing >99% of biofilm-associated S. aureus from 5% mg ml−1 after 10 minutes exposure. Cell toxicity studies with CPC-quatsomes in Nuli-1 cells revealed no adverse effects at all tested CPC concentrations. CPC-quatsomes, therefore, have a promising potential as novel drug delivery systems with “built-in” anti-biofilm activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...