Highly flexible heparin-modified chitosan/graphene oxide hybrid hydrogel as a super bilirubin adsorbent with excellent hemocompatibility†
Abstract
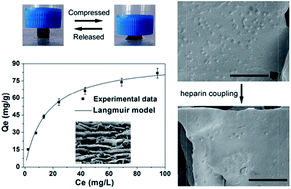
As a pathogenic toxin, bilirubin is generally removed from blood by hemoperfusion for the remission of liver disease or to gain time for patients waiting for liver transplantation. However, the development of bilirubin adsorbents with excellent mechanical properties, adsorption performance and hemocompatibility is still a considerable challenge. In this work, a heparin-modified chitosan/graphene oxide hybrid hydrogel (hep-CS/GH) has been developed for bilirubin adsorption using a lyophilization–neutralization–modification strategy. The as-prepared hybrid hydrogel displayed a unique foam-like porous structure and excellent mechanical flexibility. It was revealed that the incorporation of graphene oxide into the chitosan matrix enhanced both the compressive strength and the Young's modulus of the hybrid hydrogel, as well as its adsorption capacity for bilirubin. The maximum adsorption capacity of hep-CS/GH for bilirubin was 92.59 mg g−1, according to the Langmuir isotherm model. It was demonstrated that hep-CS/GH successfully competed with albumin, and could effectively adsorb bilirubin from a bilirubin-enriched serum. After the hydrogel was modified with heparin, protein adsorption, platelet adhesion and hemolysis were reduced, and the plasma clotting time was prolonged from 4.1 to 23.6 min, indicating the superior hemocompatibility of hep-CS/GH. Therefore, this study may pave the way for improving the performance of the adsorbent in removing blood toxins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...