Effects of 4-tert-butylpyridine on perovskite formation and performance of solution-processed perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
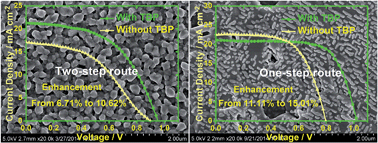
To obtain highly efficient perovskite solar cells (PSCs), effective controls on perovskite crystallinity, homogeneity, and surface morphology are crucial. Herein, we demonstrate the flexible and facile use of TBP to improve the crystallinity of perovskite in two-step or one-step routes. For the two-step route, addition of TBP into DMF when dissolving PbI2 for spin-coating resulted in a porous layer composed of randomly packed PbI2 nanocrystals. This approach subsequently offered a widely enlarged contact area facilitating interfacial reaction with CH3NH3I and greatly improved CH3NH3PbI3 crystallization. Based on this strategy, PCEs of CH3NH3PbI3-based PSCs were improved from 6.71% to 10.62% (i.e., 58% enhancement). For the one-step route, TBP as an additive resulted in orientational and better crystallinity, by which the PCEs of CH3NH3PbI3−xClx-based planar PSCs increased from 11.11% to 15.01%, showing a remarkable enhancement as high as 35%. Using TBP as one multifunctional additive, it is thought that our strategy in this work offers a new idea for the fabrication of highly efficient PSCs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...