Selection strategy of porphyrins for achieving thermally stable polymer solar cells†
Abstract
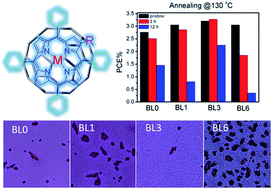
Thermal stability is an important issue of polymer solar cells (PSCs), especially for the large scale PSCs in potential real application. A new strategy of introducing porphyrin compounds to prevent fullerene aggregation and stabilize device performance under thermal stress has previously been proposed by this group. However, the effect of the porphyrin chemical structure on thermal stability still remains unclear, and the decreased power conversion efficiency (PCE) resulting from porphyrin addition needs to be overcome. In the present work, different types of porphyrins, including β-substituted and/or metallized ones, were selected, and their interactions with fullerene were first theoretically simulated, and then the morphology stability of porphyrin/fullerene binary blend films was quantitatively studied. In addition, the effect of porphyrin properties, such as self-aggregation and photo-thermal stability, was also investigated. It was eventually found that porphyrin BL3, which is –NO2-substituted and Cu-metallized, was the most promising candidate for improving the thermal stability while simultaneously keeping the device PCE higher than that of the ones without porphyrins. This porphyrin selection strategy, which has also demonstrated the feasibility for the P3HT:PC71BM system, is wished to be the stepping-stone in the study on the thermal stability of photovoltaic devices and push forward the PSC real application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...