Scaffolding an ultrathin CdS layer on a ZnO nanorod array using pulsed electrodeposition for improved photocharge transport under visible light illumination†
Abstract
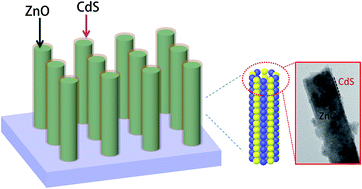
An ultrathin layer of CdS (∼8 nm) was successfully coated on an array of vertically aligned ZnO nanorods using pulsed electrodeposition. The pulse was essential during the deposition of CdS to ensure equilibrium between diffusion and nucleation of CdS precursors. These ZnO nanorods functioned as a large contact base for the deposition of CdS. This enlarged interface between CdS and ZnO together with its close intimacy facilitated efficient charge transfer from the excited CdS to ZnO upon visible illumination. Owing to the high electron mobility of ZnO, it shuttled the electrons efficiently for enhanced photocurrent generation. Compared to the bare CdS film, the CdS–ZnO photoelectrode yielded a doubled anodic visible photocurrent density of 6 mA cm−2 at 0 V vs. Ag/AgCl. Photoluminescence spectroscopy and photoelectrochemical characterization showed that the charge recombination within CdS was suppressed and the appropriate band alignment favored the electron transfer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...