Highly regenerable alkali-resistant magnetic nanoparticles inspired by mussels for rapid selective dye removal offer high-efficiency environmental remediation†
Abstract
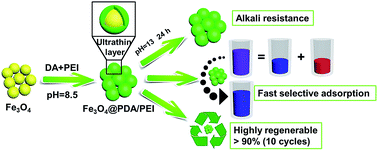
Most recently, polydopamine (PDA) and its hybrid nanomaterials have been developed as promising adsorbents to remove organic dyes. However, PDA-based adsorbents are typically limited by a poor alkali resistance, lack of selective adsorption capacity and unsatisfactory recyclability. Herein, novel PDA-based magnetic nanoparticles are fabricated for the first time via the simultaneous incorporation of PDA and poly(ethylenimine) (PEI) on Fe3O4 nanoparticles simply in one step to overcome almost all the disadvantages of “traditional” PDA adsorbents. The constructed PDA-based magnetic nanoparticles have an ultrathin shell layer (only about 3 nm, much thinner than that of other PDA adsorbents) and can withstand strong alkaline solutions (0.1 M NaOH, pH = 13), exhibiting an excellent alkali resistance. Remarkably, the nanoparticles show superior performance in smart and fast selective removal (>95% in just five minutes) of anionic dyes from dye mixtures and can maintain their high efficiency (>90%) even after 10 cycles, indicating the unprecedented selective adsorption capacity and the desirable recyclability. The adsorption process follows pseudo-second order reaction kinetics, as well as the Langmuir isotherm, indicating that anionic dyes are monolayer adsorbed on the hybrid by electrostatic interaction. In particular, the facile regeneration of the novel composite nanoparticles can be accomplished within only several minutes, demonstrating an excellent regeneration ability. Our study can provide new insights into utilizing mussel-inspired materials for environmental remediation and creating advanced magnetic materials for various promising applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...