Thermoelectric and electrical transport properties of Mg2Si multi-doped with Sb, Al and Zn
Abstract
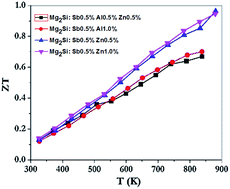
Enhanced thermoelectric and electrical transport properties of Mg2Si-based thermoelectric materials have been achieved by multi-doping with Sb, Al and Zn. Results on the investigation of the electrical transport and thermoelectric properties of multi-doped samples prepared using the spark plasma sintering technique are reported. Synchrotron radiation powder X-ray diffraction was used to characterize the structures of the doped samples. The electrical transport properties were determined from mid-infrared reflectivities, Hall effect and conventional quasi-four probe conductivity measurements. Using the electron concentrations (N) determined from the Hall coefficients, the effective masses (m*) were calculated from the frequency of the plasma edge (ωP) of the infrared reflectivities. The thermoelectric performance and thermoelectric figure of merits (ZT) in the temperature range of 300 K to 900 K of the doped Mg2Si compounds were calculated from the measured temperature dependent electrical conductivity (σ), Seebeck coefficient (S), and thermal conductivity (κ). A maximum ZT of 0.964 was found for Sb0.5%Zn0.5% doped Mg2Si at 880 K. This value is comparable to those of PbTe based thermoelectric materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...