Fabrication of oleophobic paper with tunable hydrophilicity by treatment with non-fluorinated chemicals†
Abstract
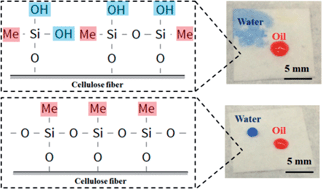
Hydrophilic-oleophobic surfaces have attracted significant attention recently due to their potential use in technologies ranging from oil–water separation to self-cleaning surfaces. However, existing methods rely heavily on fluorinated coating materials, which are harmful to the environment. In this manuscript, a simple, solution based method to fabricate oleophobic paper with tunable hydrophilicity using a non-fluorinated material is reported for the first time. Wetting control is achieved by paper surface modification using a thin film of hydrolyzed methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS). Hydrophilicity is tuned by adjusting the sonication time during MTMS hydrolysis. 29Si NMR and ATR-FTIR analyses reveal that the change in hydrophilicity is caused by varying the concentration of polar silanol groups in the MTMS solution and, ultimately, on the film surface. The modified paper displays wetting behavior ranging from superhydrophilic/oleophobic (immediate water absorption; motor oil contact angle, 64.2° ± 1.4°) to amphiphobic (water contact angle 85.2° ± 3.4°; motor oil contact angle 61.2° ± 2.5°) as a function of hydrolysis time. For all surface-modified samples, no absorption of motor oil is observed for several weeks, indicating stable oil resistance. Based upon results from SEM, optical profilometry, and air permeability, the intrinsic porosity of paper is also largely retained after coating.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...