Electrochemical properties of all-solid-state lithium batteries with amorphous MoS3 electrodes prepared by mechanical milling†
Abstract
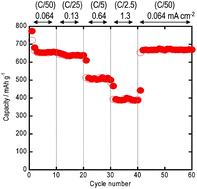
Amorphous molybdenum trisulfide (MoS3) active materials were successfully prepared by ball milling the mixture of Mo metal and sulfur. The atomic ratio of Mo to S in the starting mixture was 1 : 3. All the diffraction peaks due to the Mo metal and sulfur disappeared in the milled sample. In addition to a halo pattern due to the amorphous structure, it is a broad peak at about 15° that appeared in the diffraction profile obtained by milling for 80 hours. The HR-TEM image revealed that the microstructure of the milled sample was characterized as random distribution of nano-sized domains with the size of 2–3 nm, which consist of crystalline MoS2 with the layered structure. The DTA curve of the amorphous MoS3 exhibited no endothermic peaks attributable to the melting of crystalline sulfur. The particle size of the amorphous MoS3 was about 1 μm. All-solid-state lithium secondary batteries using a sulfide solid electrolyte and the amorphous MoS3 electrode showed capacities higher than 670 mA h g−1 for 60 cycles. The amorphous MoS3 had a higher capacity than the cell using the crystalline MoS2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...