Microporous covalent triazine polymers: efficient Friedel–Crafts synthesis and adsorption/storage of CO2 and CH4†
Abstract
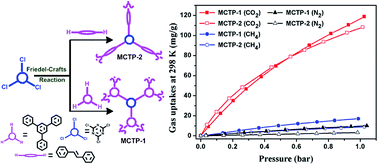
Two kinds of microporous covalent triazine-based organic polymers (MCTPs) were synthesized from inexpensive starting materials via a simple and cost effective Friedel–Crafts reaction route, and their CO2 and CH4 gas uptake capacities were investigated. The synthesized microporous materials showed high BET surface areas of 1452 (MCTP-1) and 859 m2 g−1 (MCTP-2). MCTP-1 exhibited a significant CO2 uptake capacity (204.3 mg g−1, 273 K/1 bar) with moderate CO2/N2 selectivity (15.4), whereas MCTP-2 showed a moderate CO2 uptake capacity (160.6 mg g−1, 273 K/1 bar) but exceptional CO2/N2 selectivity (68.6). MCTP-1 also exhibited substantial CO2 (497.4 mg g−1) and CH4 (85.4 mg g−1) storage capacities at 300 K and 35 bar.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...