Dynamic hydrophobic hindrance effect of zeolite@zeolitic imidazolate framework composites for CO2 capture in the presence of water†
Abstract
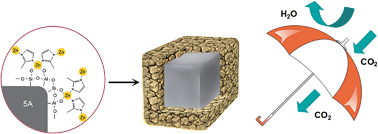
For the real industrial process of CO2 capture, it is still a great challenge for adsorbents to exhibit excellent CO2 adsorption capacity in the presence of water. By combining a pre-seeding process and a two-step temperature controlling crystallization, a zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) shell is introduced on the commercial zeolite adsorbent (5A) core to produce a series of 5A@ZIF-8 composites with an enhanced surface hydrophobicity. Each 5A@ZIF-8 composite exhibits a dynamic hydrophobic hindrance effect for the separation of CO2 from the simulated humid flue gas (15% CO2 and 90% humidity at 298 K). Among these, the CO2 adsorption capacity and the CO2/H2O selectivity of 5A@ZIF-8(I) can be as high as 2.67 mmol g−1 and 6.61, respectively, at the optimized adsorption time of 10 min. More importantly, over 10 adsorption–desorption cycles, there is almost no degradation of the adsorption performance. Therefore, the novel strategy of utilizing the dynamic hydrophobic hindrance effect through a core–shell structure would be a good solution for improving the CO2 separation performance in practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...