Brand new P-doped g-C3N4: enhanced photocatalytic activity for H2 evolution and Rhodamine B degradation under visible light†
Abstract
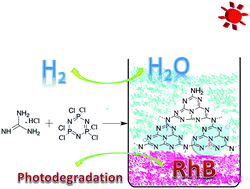
P-doped g-C3N4 has been successfully synthesized using hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene, a low cost and environmentally benign compound, as phosphorus source, and guanidiniumhydrochloride as g-C3N4 precursor, via a thermally induced copolymerization route. The obtained P-doped g-C3N4 showed excellent photocatalytic performance both in the photoreduction of H2O to produce H2 and the photodegradation of Rhodamine B (RhB). H2 evolution rate on modified g-C3N4 reached 50.6 μmol h−1, which is 2.9 times higher than that of the pure g-C3N4. RhB (10 mg L−1) was completely photodegraded within 10 min. The structure and texture properties of the P-doped g-C3N4 have been investigated in detail by XRD, FTIR, TEM, EDS and STEM. With the results of XPS and 31P NMR, a possible existing form of P atom in the framework g-C3N4 has been put forward. The introduction of a P atom significantly changes the electronic property of g-C3N4 and suppresses the recombination of photogenerated charge carriers, thus improving its photocatalytic performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...