Electrophoretic deposition improves catalytic performance of Co3O4 nanoparticles for oxygen reduction/oxygen evolution reactions†
Abstract
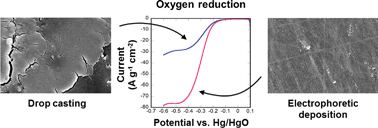
The effects of nanoparticle deposition on the catalytic activity of Co3O4 nanoparticles for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are evaluated for two deposition methods: dropcasting and electrophoretic deposition (EPD). It is found that the EPD catalyst films demonstrate better catalytic activity per unit mass than do the dropcast films, as defined by diffusion-limited current, by approximately 27% for ORR and 25% for OER. When accounting for different loading levels, the absolute activities of these catalysts are superior to those of other reported Co3O4 colloidal nanoparticulate catalysts without conductive additives, showing that this material has excellent intrinsic activity for future optimization. Inspection of the electrode kinetics shows that EPD catalysts have more favorable characteristics as exhibited by their smaller Tafel slope (96 mV per decade for EPD versus 109 mV per decade for dropcast films). We analyze this enhancement by determining the metal oxide surface area for each catalyst film using a novel sequential metal deposition technique starting with electrodeposition of Ag followed by Pb underpotential deposition (UPD). Through UPD experiments we find, surprisingly, that EPD films have a smaller surface area than the dropcast films. We conclude that EPD films are more active per unit surface area. When accounting for surface area and mass, the EPD catalyst outperforms dropcast by a factor of 2.5 for ORR and 2.6 for OER. We anticipate that morphological differences in the EPD films relative to the dropcast ones, such as particle coverage and electrical conductivity, are responsible for this behavior. Such a result has important implications for future studies on the structure of EPD-manufactured nanoparticulate thin films and on the mechanisms for performance enhancement in such catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...