Heterogeneity of single-colloid self-potentials at an oil–water interface
Abstract
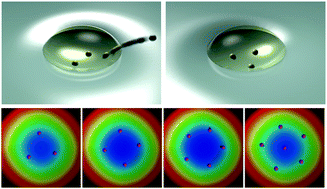
Heterogeneity in the interactions between colloidal particles at an oil–water interface is explored on a single particle level. Such a characteristic arises due to heterogeneity in self-potentials that individual particles possess. Energy minimization is numerically performed to determine the self-potentials of single colloids when the interface-trapped particles form uniquely arranged structures. We demonstrate that the obtained self-potentials correspond to the dipole strength of individual particles at the interface that can be attributed to the generation of abnormally strong and long-range repulsive interactions that should also be heterogeneous. The characterization of self-potentials on a single-particle level can potentially provide insight into the origin of heterogeneity of colloidal suspension systems at multiphasic fluid interfaces. Furthermore, the findings obtained here may facilitate an understanding of the hierarchical relationships associated with scale-dependent colloidal particle behaviors that arise due to interaction heterogeneity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...