Avalanche-like fluidization of a non-Brownian particle gel†
Abstract
We report on the fluidization dynamics of an attractive gel composed of non-Brownian particles made of fused silica colloids. Extensive rheology coupled to ultrasonic velocimetry allows us to characterize the global stress response together with the local dynamics of the gel during shear startup experiments. In practice, after being rejuvenated by a preshear, the gel is left to age for a time tw before being subjected to a constant shear rate ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) . We investigate in detail the effects of both tw and
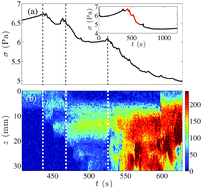
. We investigate in detail the effects of both tw and ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) on the fluidization dynamics and build a detailed state diagram of the gel response to shear startup flows. The gel may display either transient shear banding towards complete fluidization or steady-state shear banding. In the former case, we unravel that the progressive fluidization occurs by successive steps that appear as peaks on the global stress relaxation signal. Flow imaging reveals that the shear band grows until complete fluidization of the material by sudden avalanche-like events which are distributed heterogeneously along the vorticity direction and correlated to large peaks in the slip velocity at the moving wall. These features are robust over a wide range of tw and
on the fluidization dynamics and build a detailed state diagram of the gel response to shear startup flows. The gel may display either transient shear banding towards complete fluidization or steady-state shear banding. In the former case, we unravel that the progressive fluidization occurs by successive steps that appear as peaks on the global stress relaxation signal. Flow imaging reveals that the shear band grows until complete fluidization of the material by sudden avalanche-like events which are distributed heterogeneously along the vorticity direction and correlated to large peaks in the slip velocity at the moving wall. These features are robust over a wide range of tw and ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) values, although the very details of the fluidization scenario vary with
values, although the very details of the fluidization scenario vary with ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) . Finally, the critical shear rate
. Finally, the critical shear rate ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) * that separates steady-state shear-banding from steady-state homogeneous flow depends on the width of the shear cell and exhibits a nonlinear dependence with tw. Our work brings about valuable experimental data on transient flows of attractive dispersions, highlighting the subtle interplay between shear, wall slip and aging whose modeling constitutes a major challenge that has not been met yet.
* that separates steady-state shear-banding from steady-state homogeneous flow depends on the width of the shear cell and exhibits a nonlinear dependence with tw. Our work brings about valuable experimental data on transient flows of attractive dispersions, highlighting the subtle interplay between shear, wall slip and aging whose modeling constitutes a major challenge that has not been met yet.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...