Bacterial lipopolysaccharides form physically cross-linked, two-dimensional gels in the presence of divalent cations†
Abstract
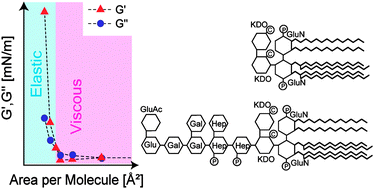
We established a bacterial membrane model with monolayers of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS Re and LPS Ra) and quantified their viscoelastic properties by using an interfacial stress rheometer coupled to a Langmuir film balance. LPS Re monolayers exhibited purely viscous behaviour in the absence of calcium ions, while the same monolayers underwent a viscous-to-elastic transition upon compression in the presence of Ca2+. Our results demonstrated for the first time that LPSs in bacterial outer membranes can form two-dimensional elastic networks in the presence of Ca2+. Different from LPS Re monolayers, the LPS Ra monolayers showed a very similar rheological transition both in the presence and absence of Ca2+, suggesting that longer saccharide chains can form 2D physical gels even in the absence of Ca2+. By exposure of the monolayers to the antimicrobial peptide protamine, we could directly monitor the differences in resistance of bacterial membranes according to the presence of calcium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...