Formation, compression and surface melting of colloidal clusters by active particles†
Abstract
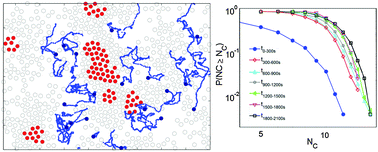
We demonstrate with experiments and numerical simulations that the structure and dynamics of a suspension of passive particles is strongly altered by adding a very small (<1%) number of active particles. With increasing passive particle density, we observe first the formation of dynamic clusters comprised of passive particles being surrounded by active particles, then the merging and compression of these clusters, and eventually the local melting of crystalline regions by enclosed active particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...