Structural rearrangement in the aqueous solution of surface active ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate
Abstract
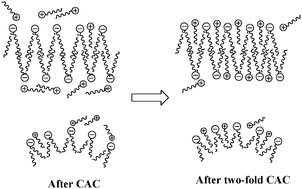
The aggregation behaviors of surface active ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate in aqueous solutions were investigated by conductometry, densimetry, fluorimetry, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which confirmed two distinguished critical concentrations. The first critical concentration was believed to be the critical aggregation concentration (CAC), where two different types of aggregates were formed, namely, micelles with the size of 10 nm and vesicles with the size of 100 nm. The second critical concentration at two-fold CAC was suggested to be resulting from the insertion of the imidazolium cations into aggregates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...