Extremely strong tubular stacking of aromatic oligoamide macrocycles†
Abstract
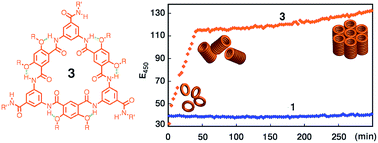
As the third-generation rigid macrocycles evolved from progenitor 1, cyclic aromatic oligoamides 3, with a backbone of reduced constraint, exhibit extremely strong stacking with an astoundingly high affinity (estimated lower limit of Kdimer > 1013 M−1 in CHCl3), which leads to dispersed tubular stacks that undergo further assembly in solution. Computational study reveals a very large binding energy (−49.77 kcal mol−1) and indicates highly cooperative local dipole interactions that account for the observed strength and directionality for the stacking of 3. In the solid-state, X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirms that the aggregation of 3 results in well-aligned tubular stacks. The persistent tubular assemblies of 3, with their non-deformable sub-nm pore, are expected to possess many interesting functions. One such function, transmembrane ion transport, is observed for 3.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...