Adsorption of toxic acidic dye from aqueous solution onto diethylenetriamine functionalized magnetic glycidyl methacrylate-N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide†
Abstract
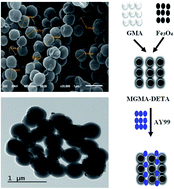
Magnetic sorbent microgranules with magnetite (Fe3O4) core and glycidyl methacrylate/N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide shell were prepared (MGMA). Diethylenetriamine (DETA) was successfully grafted (through a relatively simple solution reaction) onto the magnetic microgranules to obtain a sorbent (MGMA–DETA) with a very high content of amine groups. The obtained sorbent (MGMA–DETA) was characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). This material showed high affinity for Acid Yellow 99 dye (AY99) uptake from aqueous solutions: the maximum sorption capacity reached 0.25 mmol g−1 at pH 3.0 and ambient temperature (i.e., 25 ± 1 °C). Uptake kinetics and sorption isotherms were obtained and modeled using conventional and simple equations: the best results were respectively obtained with the pseudo-second order rate equation and the Langmuir equation. The distribution coefficient was obtained at different temperatures and the thermodynamic parameters have been calculated: the sorption is endothermic, spontaneous (especially at high relative temperature) and contributes to increase the entropy (randomness) of the system. NaOH solution (1.0 M) was used for AY99 desorption from loaded sorbents, and the sorbent could be efficiently recycled for a minimum of three sorption/desorption cycles. Therefore, MGMA–DETA could serve as a promising adsorbent for AY99 removal from industrial wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...