Ni2+ and Ti3+ co-doped porous black anatase TiO2 with unprecedented-high visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation performance†
Abstract
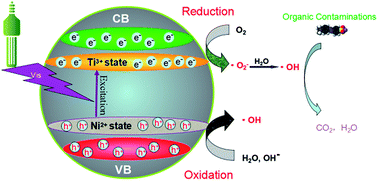
A novel Ni2+ and Ti3+ co-doped porous black anatase TiO2 is successfully synthesized by a facile sol–gel technique combined with an in situ solid-state chemical reduction approach, followed by mild calcinations (350 °C) in argon atmosphere. The obtained photocatalysts are characterized in detail by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, electron paramagnetic resonance, N2 adsorption, and transmission electron microscopy. The results indicate that the Ni2+ and Ti3+ elements are co-doped into the lattice of anatase TiO2. The prepared Ni2+/Ti3+ co-doped black anatase TiO2 possesses a mesoporous structure, consisting of disordered Ti3+ and oxygen vacancy layers. Based on UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra and valence band analysis, the doped Ni2+ and Ti3+ species can significantly narrow the band gap of anatase TiO2 due to the formation of mid-gap states, which allows utilization of visible-light and prevents fast recombination of photogenerated charges effectively. Furthermore, the prepared co-doped photocatalysts exhibit unprecedented higher photocatalytic activity than that of the pure TiO2 and the Ni2+ doped TiO2. The degradation ratio of methyl orange and rhodamine B is up to 95.38 and 95.86%, respectively, within 150 min irradiation of visible-light by the obtained Ni2+/Ti3+ co-doped porous black anatase TiO2. The high visible-light photocatalytic degradation performance may be ascribed to the efficient doping of Ni2+ and Ti3+ in favor of the absorption of visible-light and the separation of photogenerated charges, and the porous structure facilitating the diffusion of reactants and products.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...