Sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions based on papain and 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
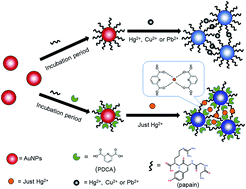
Here we demonstrate the rational design of a sensitive and selective colorimetric method for mercury ion (Hg2+) detection by using papain and 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid (PDCA) functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Papain is a protein with seven cysteine residues and 212 amino acid residues, which can combine with Hg2+, and PDCA is a chelating ligand, which has a strong affinity for Hg2+. Selectivity measurements reveal that the sensor is specific for Hg2+ even with interference by high concentrations of other metal ions. This sensor was also used to detect Hg2+ ions from real samples of tap water, river water, and pond water spiked with Hg2+ ions, and the results showed good agreement with the found values determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. The absorbance ratio (A650/A520) was linear with the Hg2+ concentration in the range of 0.01 μM to 14 μM. Under the optimum conditions (1.0 × 10−7 M papain, 5.0 × 10−4 M PDCA, pH 6.0 at 30 °C), the detection limit of Hg2+ was as low as 9 nM, which met the maximum allowable standard of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set in drinking water. In conclusion, the P-PDCA-AuNPs sensor can be used to detect the concentration of Hg2+ with high sensitivity and good selectivity, and it can lead to dramatically improved colorimetric sensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...