Structural and electronic properties of alkali metal peroxides at high pressures†
Abstract
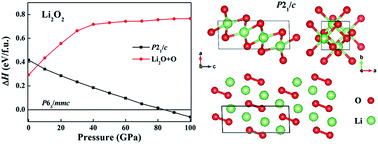
Alkali metal peroxides have a wide range of industrial applications (e.g., energy storage and oxygen source). It is well known that pressure can cause profound structural and electronic changes, leading to the fundamental modification of the physical properties. Here, we reported the structural phase transition, lattice dynamics, and electronic properties of alkali metal (Li, Na, K, and Rb) peroxides by using the unbiased structure searching techniques and first-principles density functional calculations in the pressure range of 0–100 GPa. The predicted first-order phase transitions pressures in Li2O2, Na2O2, K2O2 and Rb2O2 occur at ∼84, 28, 7 and 6 GPa, respectively, which closely correlates with the electronegativity of alkali metals. Different phase transition mechanisms and complex phase transition structures have been observed for these alkali metal peroxide compounds. These predicated high-pressure phases are thermodynamically stable against decomposition into alkali metal oxides plus O2 or alkali metals plus O2. Interestingly, the character of the peroxide group (O22−) is maintained under the considered pressure range. Phonon calculations using the quasi harmonic approximation confirm that these structures are dynamically stable. The band gaps for the studied alkali metal peroxides increase with increasing pressure. This work provides an opportunity for understanding the structures and electron properties of alkali metal peroxides at high pressures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...