Efficient and controllable synthesis of highly substituted gelatin methacrylamide for mechanically stiff hydrogels†
Abstract
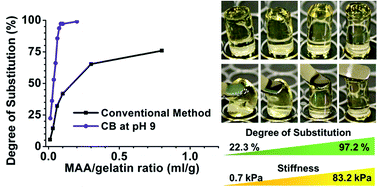
We report an effective and novel method to controllably produce highly substituted gelatin-MA with nearly 100% degree of substitution despite the use of a very low concentration of methacrylic anhydride (MAA). The method is based on sequential time-lapse loading of MAA after pH adjustment in a carbonate–bicarbonate buffer system. Rheological studies indicate that hydrogels formed from more highly substituted gelatin-MA exhibit significantly improved mechanical stiffness.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...