Understanding in crystallization of polyethylene: the role of boron nitride (BN) particles
Abstract
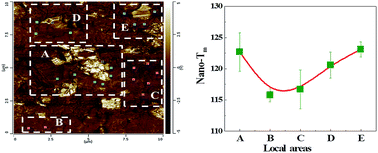
In an attempt to correctly understand an extra weak exothermic peak (Th) (near the melting temperature of the polyethylene (PE)) of the PE in the PE/boron nitride (BN) composites, a new hypothesis was proposed and proved: Th was induced by PE crystallization. When the BN content was more than 10 wt%, the Th was observed. Simultaneously, beside the Th, another weak exothermic peak (T1h), was also found. Beside the main melting peak (Tm), an extra melting peak (Tmh) also appeared. The results of the local thermal analysis technique (nano-TA) showed that the local melting temperature (nano-Tm) of the PE near the BN aggregates was higher 4–8 °C than that in other areas, indicating that the meso-phase (meso-phase was also induced by PE crystallization) can be formed near the BN aggregates during the PE crystallization. Moreover, the appearance of the Th and T1h was attributed to the differently nucleated capability of the different BN aggregates in local areas during the PE crystallization. When the annealing time and temperature were 20 min and 130 °C, respectively, the thermal conductivity of the PE/BN composite was 16% higher than that of the unannealed PE/BN composites. In addition, the results of the wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) showed that the BN particles had no influence on the PE crystal form in the PE/BN composites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...