Homogeneous vertical ZnO nanorod arrays with high conductivity on an in situ Gd nanolayer†
Abstract
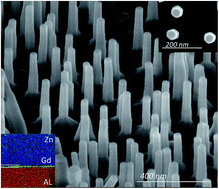
We demonstrate a novel, one-step, catalyst-free method for the production of size-controlled vertical highly conductive ZnO nanorod (NR) arrays with highly desirable characteristics by pulsed laser deposition using a Gd-doped ZnO target. Our study shows that an in situ transparent and conductive Gd nanolayer (with a uniform thickness of ∼1 nm) at the interface between a lattice-matched (11−20) a-sapphire substrate and ZnO is formed during the deposition. This nanolayer significantly induces a relaxation mechanism that controls the dislocation distribution along the growth direction; which consequently improves the formation of homogeneous vertically aligned ZnO NRs. We demonstrate that both the lattice orientation of the substrate and the Gd characteristics are important in enhancing the NR synthesis, and we report precise control of the NR density by changing the oxygen partial pressure. We show that these NRs possess high optical and electrical quality, with a mobility of 177 cm2 (V s)−1, which is comparable to the best-reported mobility of ZnO NRs. Therefore, this new and simple method has significant potential for improving the performance of materials used in a wide range of electronic and optoelectronic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...