Experimental and theoretical investigations of Michelia alba leaves extract as a green highly-effective corrosion inhibitor for different steel materials in acidic solution†
Abstract
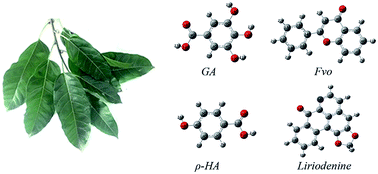
The aqueous Michelia alba leaf extract (MALE) was first evaluated as an inhibitor to the corrosion of different steel materials (industrial pure iron, stainless steel and carbon steel) in hydrochloric acid. The adsorption and corrosion inhibition of MALE were investigated by potentiodynamic polarization, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and quantum chemical calculations. The results showed that MALE acted as a highly-efficient mixed-type inhibitor for all steels and increasing temperatures benefited its corrosion inhibition. The adsorption of MALE on steel surfaces obeyed a Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Quantum chemical calculation results provided reasonable theoretical explanation for the inhibition property of MALE.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...