Synthesis of novel 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazolo-bosentan derivatives – evaluation of antimicrobial and anticancer activities and molecular docking†
Abstract
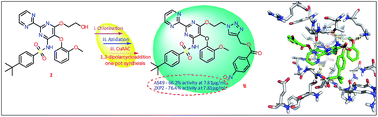
Novel 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazolo bosentan derivatives 1a–n from bosentan 2 were synthesized in good yields by sequential chlorination, azidation followed by Cu(I) catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. All obtained compounds 1a–n were evaluated for their antimicrobial and in vitro anticancer activities and by in silico docking studies. Among all tested compounds 1e,f and 1h–j show better antimicrobial activities against the tested bacteria and fungi. When subjected to anticancer testing, compounds 1g–j and 1n show significant activities against both A549 and SKOV-3 cell lines with IC50 values at 7.81 μg mL−1 and among them compound 1i exhibited very potent activity. In addition, no toxicity was calculated up to 2 mg mL−1 in Vero cells. In silico studies were conducted to investigate the possible bonding modes of 1a–n with target receptors namely DNA topoisomerase IV (4 EMV) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (2XP2). Among them, compounds 1e and 1h show maximum binding energies with 4EMV and 2XP2 receptors, respectively which also exhibited good antimicrobial and potent anticancer activities.
- This article is part of the themed collection: A Decade of Progress in Click Reactions Based on CuAAC

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...