Selective extraction of metallic arc-discharged single-walled carbon nanotubes by a water soluble polymethylsilane derivative†
Abstract
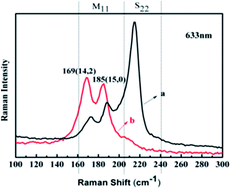
Water soluble polymethyl(1-undecylic acidyl)silane, synthesized by the hydrosilylation of 10-undecylenic acid with polymethylsilane catalyzed by 2,2′-azobisisbutyronitrile, demonstrates selective extraction ability toward metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) produced by the arc discharge method. After heating in air at a temperature of 673 K and treatment with concentrated hydrochloric acid, the arc-discharged SWNTs are ultrasonically dispersed in an aqueous solution of polymethyl(1-undecylic acidyl)silane. Such obtained dispersions are subjected to ultracentrifugation, and then the supernatant is collected. Optical absorption spectra show that the supernatant is enriched in the metallic SWNTs. Moreover, Raman spectra confirm the selective extraction of (14,2), (15,0), (13,1), (12,3) and (19,1) metallic SWNTs, which have larger diameters and smaller chiral angles than those reported previously. Additionally, FT-IR spectroscopy and Raman scattering evidence the charge transfer between polymethyl(1-undecylic acidyl)silane and SWNTs. It is conjectured that polymethyl(1-undecylic acidyl)silane could wrap chiral-index-selectively onto SWNTs through a fairly weak CH–π interaction. Thus, we believe that the stiffness and length of main chains and side chains as well as the charge state of the polymethylsilane derivative play vital roles in the selective extraction of SWNTs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...