Hydrothermal and activated synthesis of adsorbent montmorillonite supported porous carbon nanospheres for removal of methylene blue from waste water
Abstract
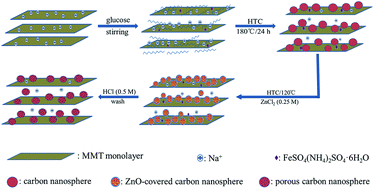
Novel adsorbent, montmorillonite supported porous carbon nanospheres (MMT-PCN) were conveniently synthesized by a hydrothermal carbonization and chemical activation treatment with ZnCl2. The as-prepared MMT-PCN material was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and N2 adsorption technology. The results indicated that the material possessed superior porosity with high surface area and large pore volume, which was utilized to remove methylene blue (MB) from an aqueous solution. The batch adsorption results implied that this novel MMT-PCN adsorbent exhibited greater performance (686.94 mg g−1) for the removal of MB than other adsorbents. Adsorption kinetics of MB onto the composite followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the adsorption isotherm data were fitted well to the Langmuir isotherm. Thermodynamic parameters, such as ΔG°, ΔH° and ΔS° were also determined and evaluated. In addition, the MMT-PCN composite exhibited satisfactory reusability properties after five consecutive cycles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...