Microfluidic synthesis of high-performance monodispersed chitosan microparticles for methyl orange adsorption
Abstract
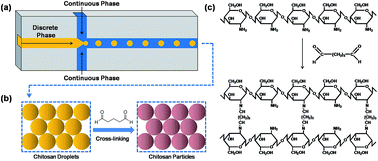
High-performance monodispersed chitosan microparticles for methyl orange (MO) adsorption were synthesized on a microfluidic platform coupled with a cross-linking approach. Batch adsorption experiments were carried out to evaluate the capacity and kinetics of the as-prepared microparticles on the adsorption of MO. Due to the advantage of microfluidics that all the manipulations and operations are related to independent droplets, the prepared microparticles are controlled to within a narrow size distribution (CV = 1.86%) while exhibiting uniform high performance (adsorption capacity = 182 mg g−1). Adsorption experiments were carried out under various design and operation conditions. It is found that the adsorption isotherm was well described by the Langmuir model and the adsorption kinetics followed a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The high performance together with biodegradable feature and low-cost raw material give the microfluidic-synthesized chitosan microparticles a promising potential for future dye effluent treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...