Chemical control of struvite scale by a green inhibitor polyaspartic acid†
Abstract
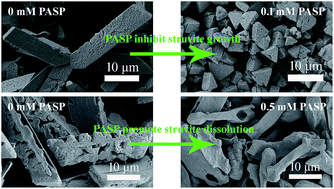
Many efforts have been made to develop effective chemical inhibitors for struvite scale, which causes a range of operational problems in the wastewater treatment industry. Herein, the inhibitory capacity of polyaspartic acid (PASP) on the spontaneous precipitation of struvite at pH 9 was investigated. Struvite precipitates were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Precipitation experiments dosed with PASP revealed that PASP is effective in the growth inhibition of struvite and its inhibitory capacity is proportional to its concentration and that PASP also plays a role in the morphological modification of struvite crystals. The effect of several key parameters, including pH, mixing energy, reaction time, and calcium ions, on PASP inhibition performance was examined for potential practical applications. The results showed that the inhibitory capacity of PASP is sustainable and efficient. Dissolution experiments dosed with PASP were also conducted, and the results showed that PASP can accelerate the dissolution of preformed struvite, and this capacity increases with an increase in its concentration. Therefore, PASP can potentially act as a feasible and environmentally-friendly inhibitor and cleaning agent for struvite scale.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...