Designing a novel high-throughput AlphaLISA assay to quantify plasma NHERF1 as a non-small cell lung cancer biomarker†
Abstract
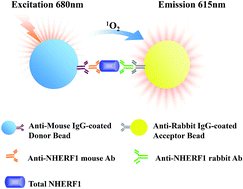
NHERF1 might play a significant role in biological processes including oncogenic transformation and metastasis. Owing to the lack of highly sensitive and quantitative methods of NHERF1 in human plasma, there have been few reports on the plasma levels of NHERF1 and its correlation with cancer. Here, a novel amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous immunoassay (AlphaLISA) has been developed and validated for the quantification of NHERF1 in human plasma. This assay was based on an AlphaScreen detection technique with two different anti-NHERF1 antibodies coupled to donor and acceptor beads, respectively. The developed AlphaLISA assay was further optimized and validated in terms of linearity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), precision, recovery, selectivity and interferences. The linear range of NHERF1 in human plasma was 5.00–100 ng mL−1, with an LOD of 2.00 ng mL−1. This AlphaLISA assay has been successfully applied to the quantification of NHERF1 in the plasma from 75 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The levels of NHERF1 protein in plasma from patients with NSCLC were significantly higher than those in the healthy group (p = 0.0004). Based on the evaluation of the ROC curves, measuring the content of NHERF1 in human plasma could provide a potential diagnostic tool for NSCLC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...