One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of carbonaceous nanocomposites for efficient decontamination of copper†
Abstract
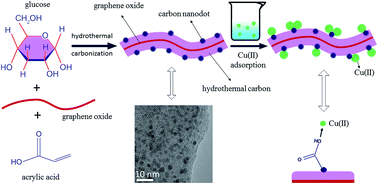
Environmental pollution associated with heavy metal ions has always been a serious environmental problem. To date, carbonaceous adsorbents are still the most promising candidates for the decontamination of these ions, but are limited by either cost or adsorption capacity. Here, carbonaceous nanocomposites containing numerous surface acidic groups were easily synthesized via one-pot hydrothermal carbonization of glucose in the presence of acrylic acid and a small amount of graphene oxide, and characterized in detail. Batch adsorption of Cu(II) on the carbonaceous nanocomposites from aqueous solution showed that these materials exhibited an excellent adsorption affinity for Cu(II) and the maximum adsorption capacity was as high as 146.1 mg g−1 at pH 5 and T = 298 K, which was much higher than any previous reports. The effect of the degree of functionality on adsorption behaviors, as well as the effects of pH, ionic strength, complex anions, temperature, and the presence of natural organic compounds (humic acid and fulvic acid) and organic pollutants (ionic liquid), were studied systematically to understand the adsorption mechanism. In addition, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was further used to confirm that surface complexation reactions played an important role in the adsorption process. This work would provide cheap nanocomposites which could be candidate materials for efficient decontamination of copper ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...