Cork extracts reduce UV-mediated DNA fragmentation and cell death†
Abstract
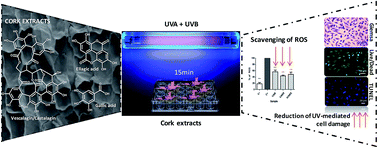
UV radiation is known to induce the premature aging of human skin and to contribute to the occurrence of different skin cancers. High doses of UVA (which is able to penetrate through the epidermis into the dermis) and/or UVB radiation (which only affects the epidermis) lead to cellular oxidative damage compromising the recovery of the normal functions of the cells. This cellular damage is mainly driven by the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that alter the redox status of the intracellular milieu, affecting the cellular metabolic activity, leading to DNA damage, apoptosis and, consequently, to a drastic decrease in the number of live cells, compromising the function of the skin. A series of polyphenolic fractions were extracted from the outer bark (cork) of Quercus suber L., and tested for their capacity to reduce the cellular damage promoted by the ROS produced during UV exposure. This was evaluated after exposing L929 fibroblasts to UV radiation in the presence and absence of the cork extracts. In all the cases the extracts at the concentration of 75 μg ml−1 demonstrated the capacity to preserve cell metabolic activity and their typical morphology, as well as to avoid DNA fragmentation after exposure to UV radiation. We were also able to correlate these findings with the intracellular reduction of ROS species and the presence of higher proportions of castalagin and vescalagin in the extracts. Our data prove that cork is a relevant source of antioxidant compounds able to act in the cellular environment, protecting cells against oxidation, reducing the number of ROS species and limiting the negative impact of UV radiation. These extracts can be further exploited in the preparation of anti-UV formulations for skin protection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...