Determination of potential main sites of apixaban binding in human serum albumin by combined spectroscopic and docking investigations†
Abstract
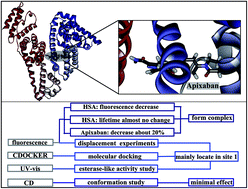
Apixaban (AP, Eliquis®) is a novel pyrazole-based direct factor Xa inhibitor. This oral drug was developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer to treat and prevent thrombotic disorders. The single crystallographic data of AP were obtained with methanol as a solvent and classified as Form N-1. The interaction of AP with human serum albumin (HSA) was investigated via different spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling. Fluorescence quenching between AP and HSA was observed to be a static process. Complexation by AP was the primary factor influencing decreases in the fluorescence intensity of HSA. AP fluorescence also decreased by approximately 20%. H-bonding and van der Waals forces played major roles in AP–HSA binding. Displacement experiments and molecular docking results demonstrated that the AP-binding site is mainly found in site 1 of HSA. The effect of AP binding on HSA esterase-like activity also confirmed this binding site. Three-dimensional fluorescence and circular dichroism studies showed that AP exerts minimal effects on the local conformation of HSA. This study provides useful information with which to better understand the utilization of AP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...