3D welan gum–graphene oxide composite hydrogels with efficient dye adsorption capacity†
Abstract
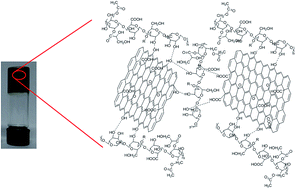
As a renewable material, welan gum is a kind of both biocompatible and biodegradable microbial polysaccharide and can be used to form polysaccharide/inorganic material composites. In this article, welan gum–graphene oxide (GO) composite hydrogels were prepared by simple self-assembly of both components in aqueous media and the effects of GO on the gelation of welan gum were systematically studied. The welan gum–GO hybrid hydrogels have been thoroughly characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and rheological measurements. It can be observed that GO is dispersed on a molecular scale in the welan gum matrix and the interactions such as hydrophobic interaction, electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding occur between the welan gum matrix and graphene oxide sheets. The addition of GO which can act as a physical cross-linker in the hydrogel and effectively promote the gelation of welan gum, can be reflected by a decrease of the critical gelation concentration (CGC). Additionally, the welan gum–GO hybrid hydrogels exhibited good adsorption properties for water-soluble dyes such as methylene blue (MB), methyl violet (MV), amido black 10B (AB10B), rhodamine 6G (R6G) and chrome azurol S (CAS). Thus, it is expected that the GO-based composite hydrogels can act as adsorbents and have promising applications in the field of waste water treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...