Overexpression of hgc1 increases the production and diversity of hygrocins in Streptomyces sp. LZ35†
Abstract
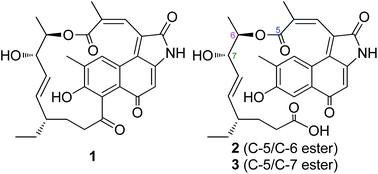
Manipulation of pathway regulation is an efficient strategy to increase the secondary metabolite production. The production of hygrocins in Streptomyces sp. LZ35 was previously increased by overexpression of the hgc1, a LAL-family pathway-specific activator gene. In this study, we have further characterized the products of the hgc1-overexpressed mutant and three new hygrocins were isolated with the aid of chromophore-guided fractionation. The structures of hygrocins H–J (1–3) were determined by the analysis of the 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic and high-resolution mass spectrometry data. Hygrocin H (1) was determined as 2,19-dehydrated-hygrocin C; hygrocin I (2) and J (3) were shown to be 13,14-seco-hygrocin H and 13,14-seco-2,19-dehydrated hygrocin F, respectively. Hygrocin H showed toxicity to human tumor MDA-MB-231, PC3 and HeLa cell lines (IC50 = 2.4, 1.7, and 0.8 μM, respectively), while hygrocins I and J were inactive at 50 μM against all the tested cell lines.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...