Aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for the efficient removal of HCV particles from human plasma samples
Abstract
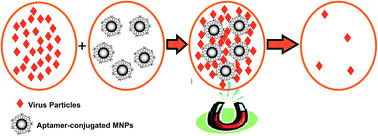
Described herein is a methodology for selectively capturing hepatitis C virus (HCV) particles from human plasma samples using aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. The aptamers were specific for binding to the E1E2 glycoprotein of HCV. The nanoconjugate was confirmed using UV-visible and FTIR spectroscopy; moreover, the transmission electron micrographs demonstrated efficient capture of these nanoconjugates using magnetic force. Also, quantitative measurement of HCV particles in human plasma samples by real-time PCR confirmed the efficient removal of the viral load.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...